In the realm of cryptocurrencies, where public ledgers document transactions, privacy is a primary concern. Consequently, privacy-enhancing technologies have surfaced to grant users heightened confidentiality and anonymity. This article delves into three notable privacy-enhancing technologies: Mimblewimble, Zcash, and Monero. Utilizing groundbreaking methods, these technologies defend user privacy and amplify the security of cryptocurrency transactions. Comprehending these technologies allows individuals and businesses to make educated choices regarding their cryptocurrency utilization while protecting their sensitive data.
What are Privacy-Enhancing Technologies?
Privacy and Cryptocurrencies
In the context of cryptocurrencies, privacy is of paramount importance. The essence of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin lies in their decentralized nature and the anonymity they can potentially offer. However, many popular cryptocurrencies aren't as private as one might think. For instance, Bitcoin transactions are publicly recorded on the blockchain, and while they are associated with pseudonymous addresses, various techniques can potentially link these addresses to the identities of individuals.
A key concern for many users is the potential for their transaction history to become publicly accessible, an issue that can lead to a variety of problems, such as exposure to targeted advertising, identity theft, or even more serious personal security threats. Therefore, enhancing privacy is a critical issue in the cryptocurrency world.
Understanding Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) in the context of cryptocurrencies are tools, protocols, and technologies designed to protect users' personal information and ensure the privacy of their transactions. They aim to reduce or eliminate the risk of unauthorized access to data, ensuring that transactions remain confidential and that users' identities are protected.
PETs can be applied at different levels and in various ways within a cryptocurrency system. They can protect the content of transactions, obscure the identity of the parties involved, or even hide the fact that a transaction took place at all.
Different cryptocurrencies implement different types of PETs, each with its own benefits and trade-offs. For instance, some may offer stronger privacy guarantees but at the cost of increased computational resources, while others may offer a balance between privacy and efficiency. The key is to choose the right tool for the job, and that's where understanding the nuances of these technologies becomes essential.
In the following sections, we will explore three distinct privacy-enhancing technologies used in Mimblewimble, Zcash, and Monero, each offering unique mechanisms to ensure transaction privacy.
Mimblewimble: Privacy Through Transaction Aggregation
What is Mimblewimble?
Mimblewimble is a privacy and fungibility-focused blockchain protocol that was introduced to the cryptocurrency community in 2016. Named after a spell from the Harry Potter series, Mimblewimble enables the creation of cryptocurrencies that enhance privacy by using a different approach to transaction structure than most other blockchains.
Rather than recording individual transactions with distinct inputs and outputs, Mimblewimble aggregates transactions, effectively 'mixing' them together. This novel approach is achieved without compromising the integrity or security of transactions, making it a fascinating case study in privacy-enhancing technologies.
How Mimblewimble Enhances Privacy
Mimblewimble achieves its privacy enhancements through a few key mechanisms. These include:
- Transaction aggregation: In a Mimblewimble-based blockchain, transactions are aggregated together before being added to a block. The aggregation process removes the separation between individual transactions, making it impossible to trace a particular transaction within a block.
- No addresses: Mimblewimble doesn't use traditional cryptocurrency addresses. Instead, two parties communicate directly with each other to construct a transaction, which is then broadcast to the network. This approach prevents the linkage of transactions to particular addresses, enhancing privacy.
- Confidential Transactions: Mimblewimble uses a cryptographic technique known as Confidential Transactions. This technique hides the amount of value being transferred in each transaction, further obfuscating the transaction details from outside observers.
Despite its privacy benefits, Mimblewimble also has its trade-offs. For instance, the absence of addresses means that Mimblewimble cannot support scripts or smart contracts in their traditional form. However, for users and applications seeking strong transaction privacy, Mimblewimble offers a compelling solution.
Zcash: Privacy Through zk-SNARKs
What is Zcash?
Zcash is a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that was launched in 2016. Built on a codebase similar to Bitcoin's, Zcash distinguishes itself by its innovative use of privacy-enhancing technologies, particularly a cryptographic concept known as zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge).
Zcash provides an option for users to choose between "transparent" transactions, which work similarly to Bitcoin, and "shielded" transactions, which offer enhanced privacy. This flexibility allows users to balance their needs for transparency and privacy as required.
How Zcash Enhances Privacy
Zcash's key privacy feature is its use of zk-SNARKs. These are proofs that allow one party to prove to another that a statement is true, without revealing any additional information beyond the truth of the statement itself. Here's how zk-SNARKs are used to enhance privacy in Zcash:
- Shielded Transactions: In a shielded transaction, the sender, receiver, and transaction amount are all encrypted. Despite this encryption, the network can verify that the transaction is valid using zk-SNARKs, without gaining any information about the transaction's details.
- Selective Disclosure: Zcash also allows for selective disclosure. This means that a user can choose to reveal some details about a transaction, such as the amount or the parties involved, to certain individuals or entities. This feature can be useful for auditing purposes or to comply with regulatory requirements.
Zcash, through its innovative use of zk-SNARKs, offers robust privacy options for users. However, it's worth noting that the privacy features of Zcash are optional and must be actively chosen by users. Additionally, creating shielded transactions requires more computational resources than transparent transactions, which can be a consideration for users. Nonetheless, for those requiring strong privacy protections, Zcash's use of zk-SNARKs provides a powerful tool.
Read our Ultimate Guide to Zero-Knowledge Proofs: zk-SNARKs vs zk-STARKs
Monero: Privacy Through Ring Signatures and Stealth Addresses
What is Monero?
Monero, launched in 2014, is a cryptocurrency that places a strong focus on privacy, decentralization, and fungibility. Unlike some cryptocurrencies where privacy is an optional feature, Monero is designed to provide privacy by default. Monero's blockchain is constructed in such a way that no observer can tell the source, amount, or destination of transactions.
Monero achieves this high level of privacy through the use of several innovative technologies. Those include ring signatures, ring confidential transactions, and stealth addresses.
How Monero Enhances Privacy
Monero's privacy enhancements can be attributed to a combination of unique features and technologies:
Ring Signatures: This technology is used to protect the sender's identity. A ring signature is a type of digital signature where a transaction is signed and verified by a group of potential signers, forming a "ring". This approach obscures the identity of the actual signer, making it virtually impossible to determine who the actual sender of a given transaction is.
Ring Confidential Transactions (RingCT): RingCT is an extension of the concept of ring signatures. In addition to hiding the sender's identity, RingCT also conceals the transaction amount, adding another layer of privacy to Monero transactions.
Stealth Addresses: Monero uses stealth addresses to protect the receiver's identity. When a transaction is made, a one-time address is created for the recipient. This address is not linked to the actual address of the recipient, thereby protecting their privacy.
Despite its strong privacy features, Monero also comes with its own set of trade-offs. For instance, due to its privacy mechanisms, the Monero blockchain is significantly larger than that of other cryptocurrencies, which can lead to issues related to storage and synchronization. Nevertheless, for those who value privacy above all else in their transactions, Monero offers one of the most comprehensive solutions in the cryptocurrency space.
Conclusion
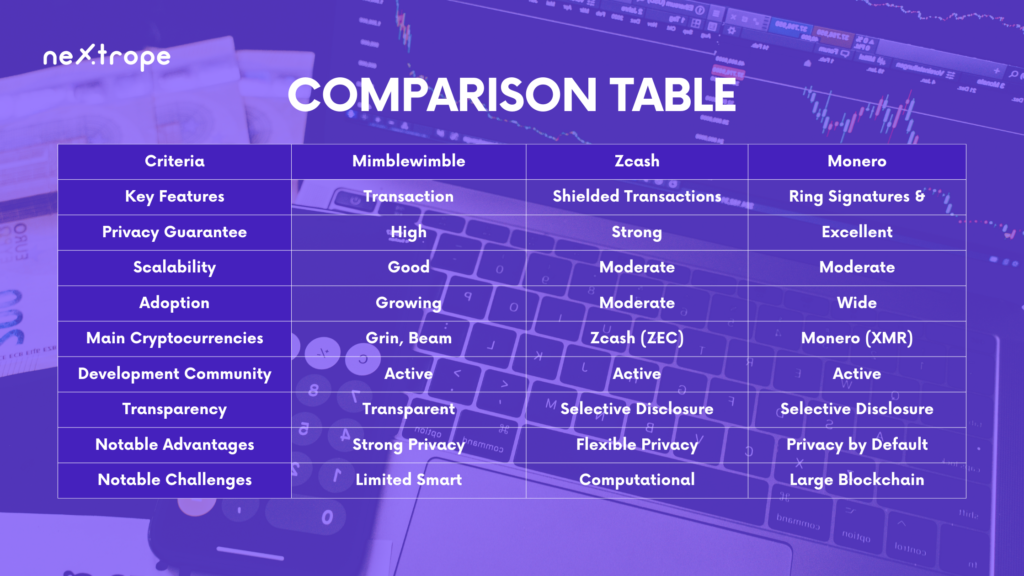
To sum up, addressing privacy concerns related to cryptocurrencies is made possible through privacy-enhancing technologies like Mimblewimble, Zcash, and Monero. These technologies implement unique approaches to preserve user privacy and bolster transaction security. By focusing on transaction aggregation in Mimblewimble, employing zk-SNARKs for shielded transactions in Zcash, and utilizing ring signatures alongside stealth addresses in Monero, individuals and businesses can comprehend these technologies and make educated decisions to safeguard their sensitive data while interacting with cryptocurrencies.
 en
en  pl
pl 







