DAO governance models is a crucial aspect of DAOs. It outlines decision-making processes, voting mechanisms, funds management, and stakeholder participation. These models have been used to fund, manage and govern DAOs in the cryptocurrency space for several years. This article will discuss the rise of DAOs and examine the various governance models adopted by these innovative organizations.
Excited about joining the DAO? Check out our guide!
Understanding DAO Governance Models
DAO governance models provide a structure for decentralized decision-making and resource allocation within an organization. These models are designed to promote transparency, inclusivity, and community-driven decision-making. Unlike traditional governance structures, where decisions are made by a select group of individuals or entities, DAOs enable broader participation, allowing stakeholders to contribute and influence decisions. Governance models are critical to the success of decentralized organizations.
DAO Governance Models - Fundamental Concepts
- Transparency: Promoting easy access to data and involvement in decision-making.
- Security: Establishing protective measures against harmful attacks or tampering within the DAO.
- Flexibility: Facilitating change and growth in response to the DAO's and its ecosystem's development.
- Inclusivity: Fostering wide-ranging community involvement and engagement of stakeholders.
Main DAO Governance Models
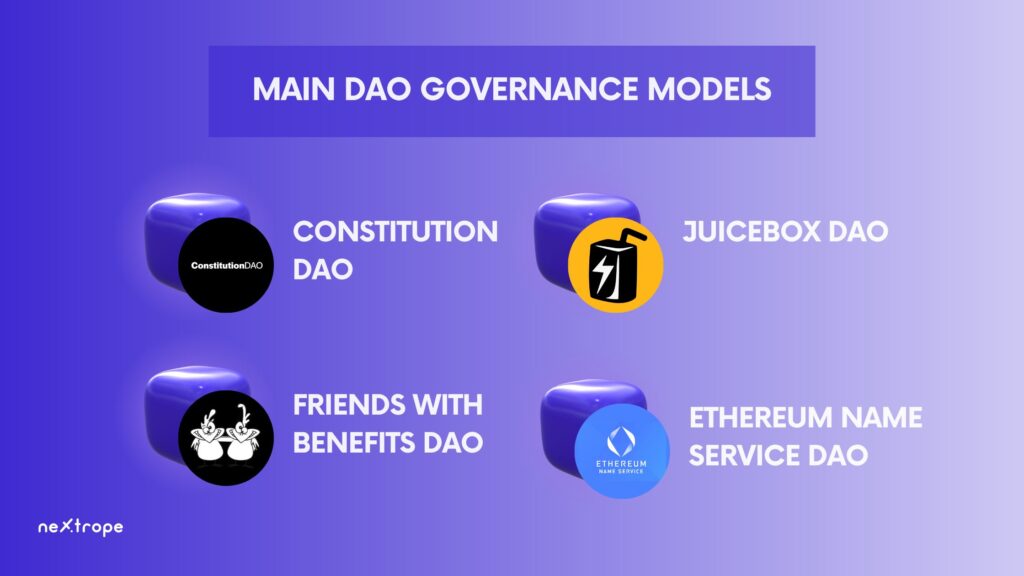
There are four main DAO governance models:
- ConstitutionDAO,
- Friends with Benefits DAO,
- JuiceboxDAO,
- Ethereum Name Service DAO.
ConstitutionDAO
ConstitutionDAO represents a governing framework that allows users to collectively pool their resources and acquire shared asset ownership through cryptocurrencies. This DAO governance arrangement ensures stability for its members by implementing a clear set of rules that dictate the DAO's operations.
As one of the first DAO governance structures, ConstitutionDAO has demonstrated the potential of decentralized organizations and the power of collective efforts in achieving shared goals.
Friends with Benefits DAO
FWB, or Friends with Benefits DAO, is a community centered around social tokens that aims to assist creators and forge solid connections between its participants. Utilizing dao governance models, FWB promotes a socially-driven approach where members holding vested tokens can partake in the decision-making process. This method highlights teamwork, repute, and the value of social capital, empowering members to jointly influence the community's path and efforts.
JuiceboxDAO
JuiceboxDAO represents a novel form of dao governance models, integrating aspects of both token-based systems and conviction voting. Within this paradigm, holders of tokens possess voting authority in relation to their stake size, while also being able to demonstrate their dedication by securing their tokens for a certain time frame. As tokens are locked for longer periods, the votes gain more influence. This method encourages lasting engagement and fosters harmony between the motives of stakeholders and the accomplishments of the DAO's projects and endeavors.
Ethereum Name Service DAO
The Ethereum Name Service (ENS) Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) offers a fully distributed domain name system built upon the Ethereum blockchain network. Its governance framework integrates a unique "proof of individuality" process, in which participants establish their distinctiveness through an identity authentication procedure. The ENS DAO employs a quadratic voting mechanism that enables token holders to apportion their voting authority across multiple proposals. In doing so, this model fosters equitable treatment and deters the centralization of power by dispersing influence more evenly among participants.
ENS DAO works on a three-layered approach:
- Discourse of proposals
- Off-chain voting used by delegates
- Voting on the blockchain
Use Cases of DAO Governance Models
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) governance models have significantly impacted the field of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi platforms often leverage DAOs to manage key protocol decisions, such as setting interest rates, defining collateral requirements, or introducing new features. Applying a DAO governance structure allows DeFi initiatives to involve community members in the decision-making process, thereby fostering a more inclusive and decentralized financial landscape.
2. Collective Investment and Fund Management
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have become valuable tools for group investment and the management of funds. With the implementation of DAO governance structures, those who hold tokens can collaboratively make investment choices, resulting in a more equitable and transparent approach to investing. These DAOs enable pooling of resources, empowering participants to team up and invest in various projects, oversee funds, and apportion profits according to predetermined rules.
3. Content Creation and Curation
In the digital content space, DAO governance models offer new opportunities for content creation and curation platforms. Utilizing DAOs allows content creators and curators to obtain rewards through community-driven voting systems and decision-making procedures. This guarantees that the most valuable and high-quality content receives recognition and financial incentives, creating a fairer and more decentralized content ecosystem.
4. Decentralized Governance
Perhaps the most fundamental use case is in decentralized governance itself. DAOs can be created to manage the decision-making processes within communities, organizations, or even entire cities. By giving power back to the people, DAOs facilitate direct democratic participation, allowing individuals to have a say in matters that affect them. This enables greater transparency, accountability, and inclusivity in governance processes.
Conclusion
DAOs have revolutionized traditional management structures, enabling decentralized decision-making and value creation. With the ability to apply different models to different sectors, such as DeFi, content platforms and investments, DAOs are able to transform and revolutionize a variety of industries.
 en
en  pl
pl