Recently we summed up all you need to know about Automatic Market Makers. Get to know their key element- liquidity pools. How do they work and what do you need to know before you decide to implement them into your decentralized exchange?
What will you find in the article?
- Role of liquidity pools in AMM
- Why liquidity pools are essential for DEXs
- How does liquidity pool work?
- LP tokens
- How to use liquidity pools?
Definition
Liquidity pools are digital assets managed by smart contracts that enable trades between different tokens or cryptocurrencies on Decentralized Exchanges. Assets are deposited there by liquidity providers - investors and users of the platform.
Liquidity pools are a backbone of Automatic Market Maker, which replaces one side of a trade with an individual liquidity pool.
Decentralized Exchanges: Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are among the most robust solutions for contemporary DeFi ecosystems. Currently, most DEXs work on the Automatic Money Maker model, and liquidity pools are a crucial part of it.
To fully understand the importance of DeFi liquidity pools, we should first look at variable ways in which DEXs can handle trading.

How do decentralized exchanges operate trading?
- On-chain order book
- Off-chain order book
- Automated Market Maker
Currently, the last of them seems to be the most effective. Therefore the vast majority of modern DEXs are based on it. Since liquidity pools are its backbone, their importance in the DeFi sector is undeniable.
Problems with ordering books
Before launching the first automated market makers, liquidity was a significant issue for decentralized exchanges, especially for new DEXs with a small number of buyers and sellers. Sometimes it was simply too difficult to find enough people willing to become a side in trading pair.
In those cases, the peer-to-peer model didn’t support liquidity on a sufficient level. The question was how to improve the situation without implementing a middle man, which would lead to losing the core value for the DeFi ecosystem - decentralization. The answer came with AMM.
Trading pairs
Let’s use the example of Ether and Bitcoin to describe how trading pairs work in the order book model on DEX.
If users want to trade their ETH for BTC, they need to find another trader willing to sell BTC for ETH. Furthermore, they need to agree on the same price.
While in the case of popular cryptocurrencies and tokens, finding a trading pair shouldn’t be a problem, things get a bit more complicated when we want to trade more alternative assets.
The vital difference between order books and automatic market makers is that the second one doesn’t require the existence of trading pairs to facilitate trade. All thanks to liquidity pools.
Role of liquidity pool in AMM
Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange protocol that relies on smart contracts to set the price of tokens and provide liquidity. In an automated market makers' model, assets are priced according to a pricing algorithm and mathematical formula instead of the order book used by traditional exchanges.
We can say that liquidity pools are a crucial part of this system. In AMM trading pair that we know from traditional stock exchanges and order book models is replaced by a single liquidity pool. Hence users trade digital assets with a liquidity pool rather than other users.
P2P VS P2C
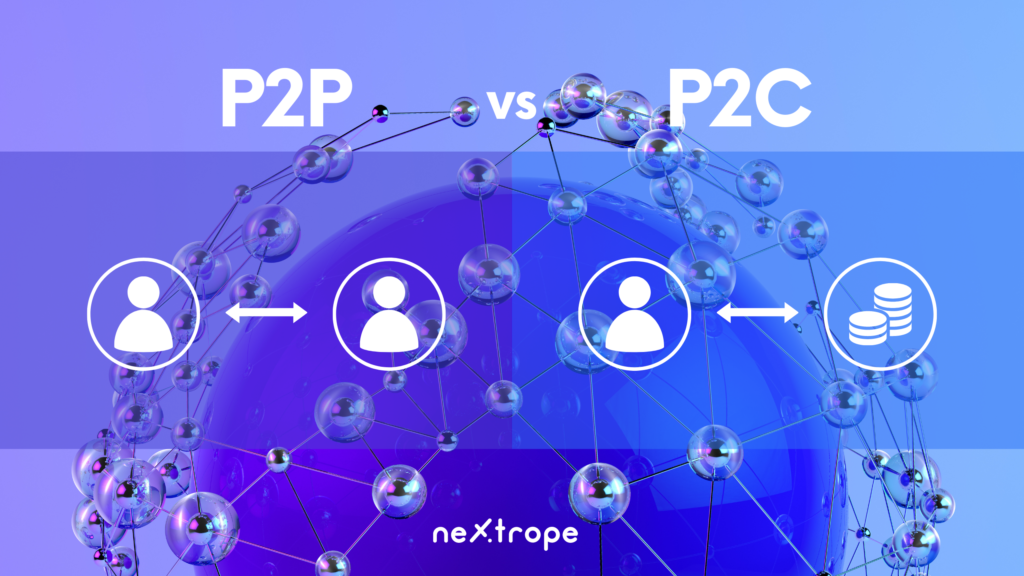
Peer-to-peer is probably one of the best-known formulas from the DeFi ecosystem. For a long time, it was a core idea behind decentralized trading.
Yet blockchain technology improvement and the creativity of developers brought new possibilities. P2C - peer-to-contract model puts smart contracts as a side of the transaction. Because smart contract can’t be influenced by any central authority after it was started, P2C doesn’t compromise decentralization.
Essentially Automated Market Makers is peer-to-contract solutions because trades take place between users and a smart contract.
Liquidity providers
Liquidity pools work as piles of funds deposited into a smart contract. Yet, where do they come from?
The answer might sound quite surprising: pool tokens are added to liquidity pools by the exchange users. Or, more precisely, liquidity providers.
To provide the liquidity, you need to deposit both assets represented in the pool. Adding funds to the liquidity pool is not difficult and rewards are worth considering. The profits of liquidity providers differ depending on the platform. For instance, on Uniswap 0.3% of every transaction goes to liquidity providers.
Gaining profits in exchange for providing liquidity is often called liquidity mining.
How do liquidity pools work?
Essentially, the liquidity pool creates a market for a particular pair of assets, for example, Ethereum and Bitcoin. When a new pool is created, the first liquidity provider sets the initial price and equal supply of two assets. This concept of supply will remain the same for all the other liquidity providers that will eventually decide to stake their found in the pool.
DeFi liquidity pools hold fair values for assets by implementing AMM algorithms, which maintain the price ratio between tokens in the particular pool.
Different AMMs use different algorithms. Uniswap, for example, uses the following formula:
a * b = k
Where 'a' and 'b' are the number of tokens traded in the DeFi liquidity pool. Since 'k' is constant, the total liquidity of the pool must always remain the same. Different AMMS use various formulas. However, all of them set the price algorithmically.
Earning from trading fees
A good liquidity pool has to be designed to encourage users to stake their assets in it. Without it supplying liquidity on a sufficient level won't be possible.
Therefore most exchanges decide on sharing profits generated by trading fees with liquidity providers. In some cases (e. g., Uniswap), all the fees go to liquidity providers. If a user's deposit represents 5% of the assets locked in a pool, they will receive an equivalent of 5% of that pool’s accrued trading fees. The profit will be paid out in liquidity provider tokens.
Liquidity provider token (LP token)
In exchange for depositing their tokens, liquidity providers get unique tokens, often called liquidity provider tokens. LP tokens reflect the value of assets deposited by investors. As mentioned above, those tokens are often also used to account for profits in exchange for liquidity.
Normally when a token is staked or deposited somehow, it cannot be used or traded, which decreases liquidity in the whole system. That’s problematic, because as I mentioned, liquidity has a pivotal value in the DeFi space.
LP tokens enable us to liquid assets that are staked and normally would be frozen until providers will decide to withdraw them. Thanks to LP tokens, each token can be used multiple times, despite being invested in one of the DeFi liquidity pools.
Furthermore, it opens new possibilities related to indirect forms of staking.
Yield Farming
Yield farming refers to gaining profits from staking tokens in multiple DeFi liquidity pools. Essentially liquidity providers can stake their LP tokens in other protocols and get for it other liquidity tokens.
How does it work?
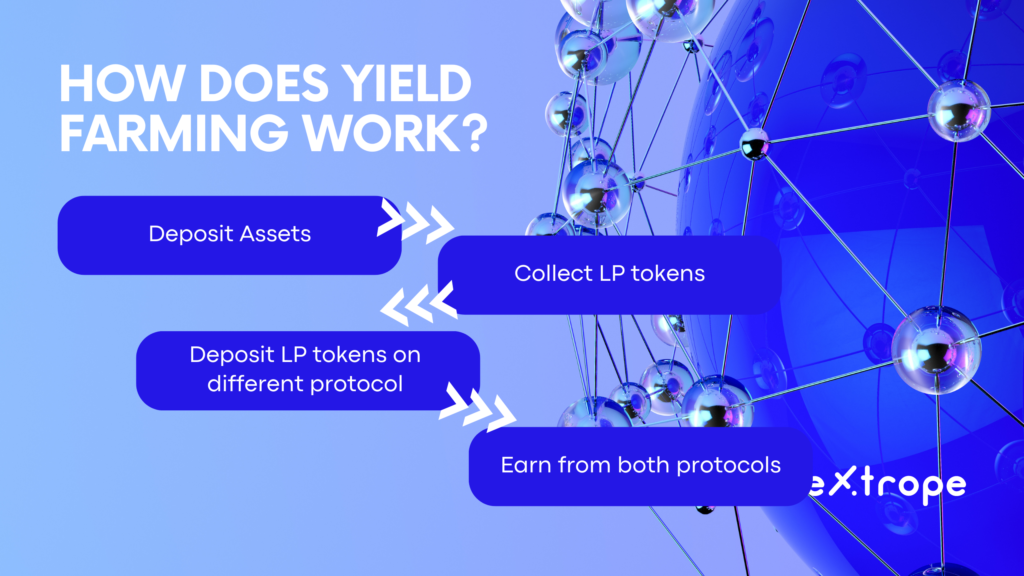
Actually, from the user perspective, it's quite simple:
- Deposit assets into a liquidity pool
- Collect LP tokens
- Deposit or stake LP tokens into a
- Separate lending protocol
- Earn profit from both protocols
Note: You must exchange your LP tokens to withdraw your shares from the initial liquidity pool.
How to use Liquidity pools in your DEX?
Decentralized finance develops at tremendous speed, constantly bringing new possibilities. The number of people interested in DeFi investments increases every day; hence the popularity of options such as liquidity mining recently has grown significantly. While deciding to launch our DEX, you have to be aware of that.
As I mentioned, liquidity has pivotal importance for decentralized finance, particularly for exchanges. Liquidity pools can't exist without investors that will add liquidity to them. Their shortage will lead to low liquidity. In consequence, that will be a cause of the low competitiveness of the exchange. On the other hand, for new DEXs it's still easier than attracting enough buyers and sellers to support order book trading.
Implementing liquidity pools to your DEX requires not only experience of blockchain developers’ fluently using DeFi protocols but also a solid and well-planned business strategy. That's why choosing a technology partner with previous experience with both blockchain development and business consulting in the decentralized finance field might be the optimal solution.
Do you want to gain more first-hand knowledge regarding liquidity pools development and implementation? Don't hesitate to ask our professionals that will gladly answer your questions.
 en
en  pl
pl 





